TDEE Calculator
Calculate your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) and get a personalized macronutrient breakdown to achieve your fitness goals.
TDEE Calculator Form
Enter your information to calculate your stats.
TDEE Calculator Results
Your Results Await
Fill out the form to see your personalized health metrics.
Table of Contents
Jump to the section you're interested in.
What is TDEE and Why It Matters for Your Fitness
TDEE stands for Total Daily Energy Expenditure. It is the total number of calories your body burns in a 24-hour period, including all activities—from sleeping and breathing to intense exercise. Understanding your TDEE is the most critical first step in taking control of your health, whether your goal is to lose fat, build muscle, or maintain your current weight.
Key Takeaways About Your TDEE
- Your TDEE is the total number of calories your body burns in a day.
- It combines your resting metabolism (BMR) with calories burned from activity and digestion.
- Knowing your TDEE is the foundation for setting effective calorie targets for any fitness goal.
- Learn more about us and our scientific approach.
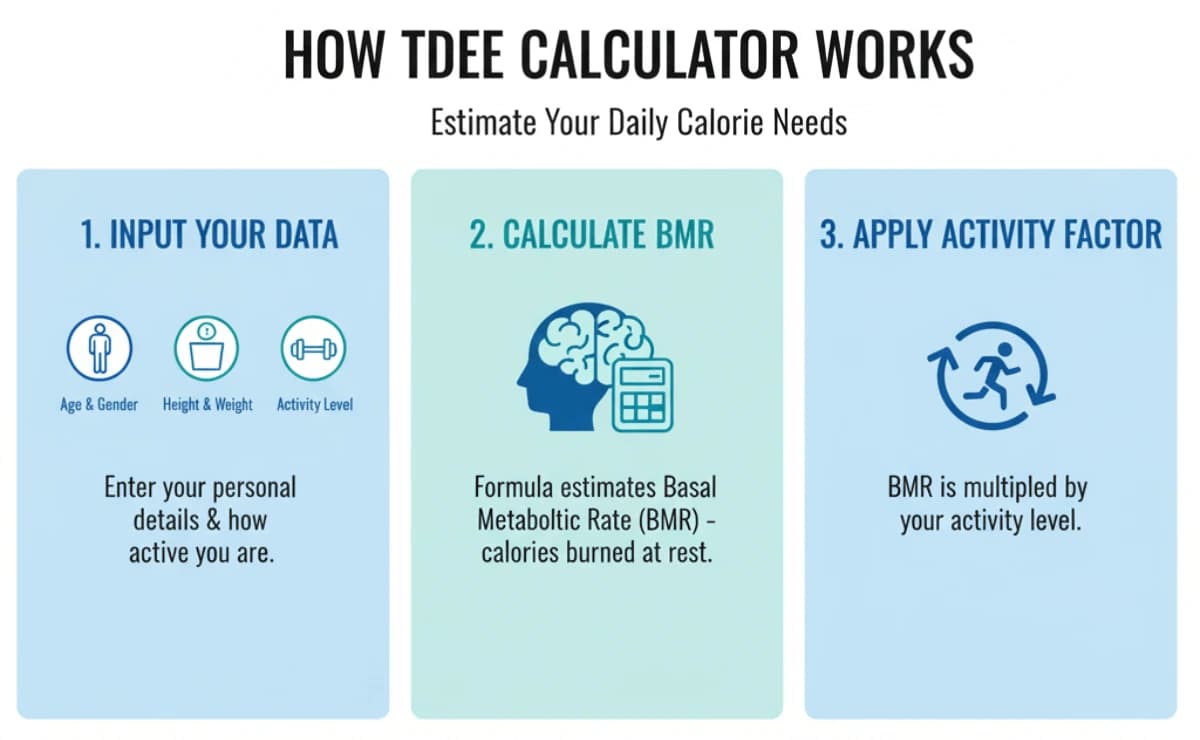
How does TDEE help with weight loss?
To lose weight, you must consume fewer calories than your body burns, creating a "calorie deficit." Your TDEE is your baseline calorie requirement. By eating consistently below your TDEE (e.g., 300-500 calories less per day), you signal your body to use its stored fat for energy, leading to sustainable weight loss.
Is TDEE better than just counting calories?
TDEE gives context to calorie counting. While counting calories tracks what you eat, your TDEE tells you *how many* calories you should be eating. Without knowing your TDEE, calorie counting is just guesswork. Using your TDEE provides a personalized, scientific target that makes your efforts far more effective.
Customize Your Goal
Use your TDEE to create a science-backed plan for your specific fitness objective.
Lose Fat
To burn fat, you need to consume fewer calories than you burn. A calorie deficit signals your body to use stored fat for energy.
Eat 15-20% below your TDEE
Maintain Weight
To maintain your current weight, you need to balance your calorie intake with your expenditure. This is your TDEE.
Eat at your TDEE
Build Muscle
To build muscle, you need to provide your body with extra energy and protein for growth. A calorie surplus is key.
Eat 10-15% above your TDEE
Our calculations are based on the Mifflin-St Jeor formula, trusted by nutritionists.
Activity Multiplication Factors
Your BMR is multiplied by an activity factor to determine your TDEE. The more active you are, the more calories you burn.
Why Choose TDEE Calculator
We've built a tool that is not only accurate but also a joy to use.
Fast & Lightweight
No ads, no lag, no distractions. Get your results instantly without unnecessary waiting.
Privacy-Focused
No signup required. Your data is stored locally in your browser and never sent to our servers.
Smart Macros Calculation
Go beyond calories with a personalized macronutrient plan to support your specific goals.
Works on All Devices
Engineered for speed. Get your results instantly on any device, from mobile to 4K displays.
Based on Scientific Formulas
Leveraging scientifically-validated formulas for BMR and TDEE results you can trust.
100% Free
All features are completely free to use. No hidden costs or premium tiers.
How to Calculate Your BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate)
BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate) is the number of calories your body burns at rest to maintain essential functions like breathing, circulation, and cell repair. In simple terms — it’s the energy your body needs to survive even if you did nothing all day.
Understanding your BMR helps you:
- Track your true calorie needs
- Plan smarter diet or weight goals
- Avoid eating too much or too little
The most accurate BMR formulas are:
1️⃣ Mifflin-St Jeor Equation (Modern & Widely Used)
For Men:
BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) - (5 × age) + 5
For Women:
BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) - (5 × age) - 161
Example:
If you’re a 30-year-old man, weighing 70 kg and 175 cm tall:
BMR = (10 × 70) + (6.25 × 175) - (5 × 30) + 5 = 1,661.25 kcal/day
This means your body burns about 1,660 calories per day at rest.
| Term | Meaning | Includes Physical Activity? |
|---|---|---|
| BMR | Energy your body burns at rest | ❌ No |
| TDEE | Total energy burned daily | ✅ Yes |
So if you work out, walk, or even do household chores — your TDEE will be higher than your BMR. You can use the TDEE Calculator on our site to find your total daily energy needs instantly.
- BMR is your body’s energy baseline.
- Calculating it helps you control weight and nutrition better.
- Combine your BMR with your activity level to find your TDEE (Total Daily Energy Expenditure).
- For the best and easiest results, use our free BMR & TDEE Calculator.
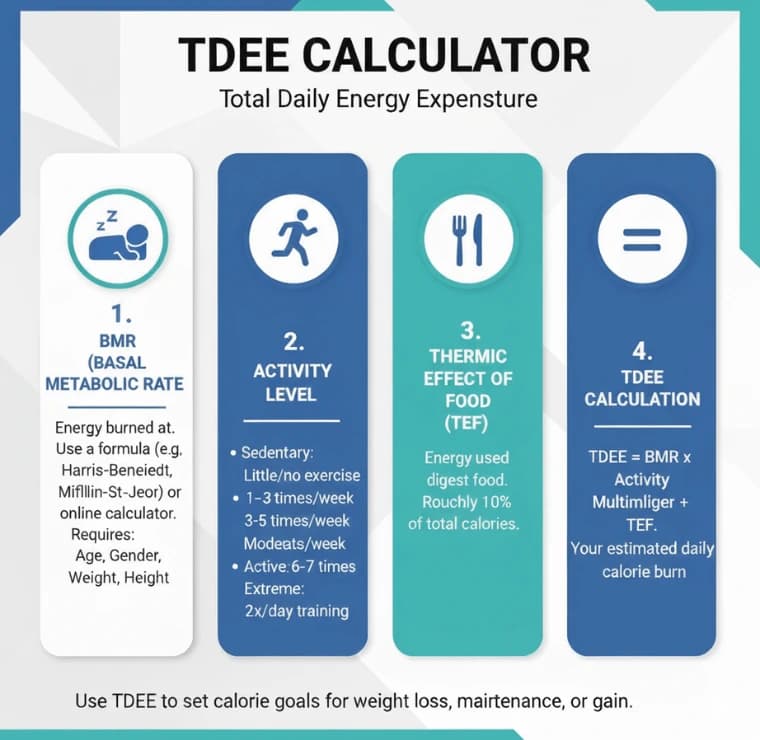
BMR vs. TDEE: What's the Difference?
While BMR is your energy at rest, TDEE accounts for your entire day. It’s the metric you should use for setting calorie goals.
Your BMR
Calories burned at rest
Physical Activity
Exercise & daily movement
Thermic Effect of Food
Calories to digest food
Your TDEE
Total Daily Energy Expenditure
In simple terms, your TDEE is the sum of your BMR and all the calories you burn through physical activity and digesting food. This is why it's a more complete and actionable number for your fitness journey.
How to Adjust Calories for Your Fitness Goals
Your TDEE is your starting line. Here’s how to cross the finish line, whether you're aiming for fat loss, muscle gain, or maintenance.
Calorie Adjustments at a Glance
| Goal | Recommended Adjustment | Example (2,500 TDEE) |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Loss | Subtract 300–500 calories (15-20% deficit) | 2,000–2,200 kcal/day |
| Maintenance | Eat at your TDEE | 2,500 kcal/day |
| Muscle Gain | Add 250–500 calories (10-15% surplus) | 2,750–3,000 kcal/day |
Pro-Tips for Success
Be Patient & Consistent
Stick to your plan for 2-4 weeks before making big changes. Results take time.
Track Your Progress
Weigh yourself 3-4 times a week under the same conditions and take the weekly average. Adjust calories by 100-200 if needed.
Listen to Your Body
If you feel constantly fatigued, your deficit might be too aggressive. Slow and steady wins the race.
Frequently Asked Questions
Calories vs. Macros
While calories determine weight gain or loss, your macronutrient breakdown determines your body composition (muscle vs. fat).
4 calories per gram
The building block for muscle. Essential for repairing tissues and preserving lean mass, especially in a calorie deficit. It is also highly satiating, helping you feel full.
Primary Sources:
Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, tofu, and protein powder.
4 calories per gram
The body's primary fuel source. Carbs provide the energy needed for high-intensity workouts and daily brain function. Complex carbs offer sustained energy.
Primary Sources:
Oats, rice, potatoes, bread, pasta, fruits, and vegetables.
9 calories per gram
Crucial for hormone production, vitamin absorption, and brain health. Healthy fats are a vital part of any diet, but are the most calorie-dense macro.
Primary Sources:
Avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon.
Ready to Know Your Calorie Needs?
Get an instant, science-backed analysis of your daily calorie and macro requirements.
